In today's digital age, the importance of computer security cannot be overstated. The threat of viruses and malware looms large, with cybercriminals constantly devising new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in your system. To safeguard your computer and personal data, it's essential to be proactive and take steps to protect your device from these malicious attacks.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore various strategies, tips, and tools to help you fortify your computer's defenses against viruses and malware. Whether you're a casual user or a tech-savvy individual, these recommendations will help you stay secure in the digital realm.
What Are Computer Viruses?
Computer viruses are malicious software programs designed to infect, spread, and potentially harm your computer. These digital parasites can take many forms, including viruses, Trojans, worms, ransomware, and spyware. Understanding the nature of these threats is vital to defending your computer.
A computer virus is a type of malware (malicious software) that, like its biological namesake, replicates and spreads to other files and systems. These viruses can disrupt your computer's normal operations and, in some cases, cause significant damage. To protect your computer effectively, you must understand the different types of computer viruses and how they function.
There are various types of computer viruses, and they often evolve to become more sophisticated and dangerous. Here are some common types of computer viruses:
- Resident Viruses: These viruses embed themselves in the memory of a computer, making them challenging to remove. They can infect multiple files and compromise system stability.
- Non-Resident Viruses: Unlike resident viruses, non-resident viruses do not embed themselves in the computer's memory. Instead, they operate through file manipulation, which can make them easier to detect and remove.
- Multipartite Viruses: These are complex viruses that employ multiple infection methods. They can infect both program files and the computer's system sectors.
- Polymorphic Viruses: These viruses have the ability to change their code or appearance to avoid detection by antivirus software. Polymorphic viruses are particularly challenging to combat.
- Metamorphic Viruses: Similar to polymorphic viruses, metamorphic viruses continually change their code to evade detection. They are among the most advanced and resilient types of viruses.
Understanding the different types of viruses is essential because each may require a specific approach for detection and removal.
How Do Viruses Infect Your Computer?
Viruses can infiltrate your system through various means, such as email attachments, infected downloads, malicious websites, and more. Once inside, they replicate and spread throughout your files and folders. Let's delve deeper into the methods by which viruses infect your computer.
- Email Attachments: Cybercriminals often use email as a vector for delivering malware. They send seemingly innocuous attachments that, once opened, can infect your system. To protect yourself, never open email attachments from unknown or suspicious sources. Even if an email appears to be from someone you know, exercise caution if the attachment seems out of the ordinary.
- Malicious Downloads: Downloading files from untrusted websites or sources can lead to virus infections. Many hackers disguise their malware as legitimate software or files, making it essential to download from reputable websites and verify the authenticity of the source.
- Infected Websites: Visiting compromised or malicious websites can expose your computer to drive-by downloads. These downloads happen automatically when you visit a site, and they can infect your computer without your knowledge. Staying away from suspicious websites and keeping your browser and plugins up to date can help prevent such infections.
- Removable Media: Viruses can spread through USB drives, external hard drives, and other removable media. Avoid using unfamiliar media on your computer, and scan any external devices for malware before opening files from them.
- Network Vulnerabilities: If your computer is connected to a network, whether at home or work, it's susceptible to viruses spread through network vulnerabilities. Keeping your network secure with firewalls and strong passwords can mitigate this risk.
The Consequences of Virus Infection
A virus infection can lead to data loss, system instability, identity theft, and even financial loss. Some viruses can hold your files hostage until you pay a ransom, while others quietly steal your personal information. The consequences of a virus infection can be severe and varied, making it crucial to understand the potential risks.
- Data Loss: Many viruses can corrupt or delete your files, causing data loss that may be irreversible. Without proper backups, important documents, photos, and other valuable data could be lost.
- System Instability: Some viruses disrupt the normal functioning of your computer, leading to system crashes, freezes, and slowdowns. These issues can be frustrating and disruptive to your work or activities.
- Identity Theft: Certain viruses, such as keyloggers, are designed to record your keystrokes and capture sensitive information like login credentials and credit card details. This information can be used for identity theft and fraud.
- Financial Loss: Ransomware viruses encrypt your files and demand a ransom in exchange for the decryption key. Paying the ransom is not recommended, as there is no guarantee that you'll regain access to your files. This can result in financial loss without a resolution.
- Reputation Damage: If a virus sends malicious or embarrassing content to your contacts or posts it online in your name, your reputation can suffer. Rebuilding trust can be a lengthy and challenging process.
Understanding these consequences can motivate you to take the necessary steps to protect your computer from viruses. In the following sections, we'll explore the specific measures and tools to secure your system effectively.
How to Protect Your Computer from Viruses
1. Antivirus Software: Your First Line of Defense
Antivirus software is a critical component of your computer's defense against viruses and other malware. Its primary function is to scan your computer for known threats, remove or quarantine them, and prevent future infections. Here's why antivirus software is your first line of defense:
- Real-Time Protection: Antivirus software provides real-time protection, constantly monitoring your computer for signs of malicious activity. If it detects a threat, it can take immediate action to block or remove it.
- Scheduled Scans: You can schedule regular scans to check for viruses and malware. These scans can run in the background or at times when your computer is typically not in use.
- Database of Known Threats: Antivirus programs maintain extensive databases of known viruses and malware. They compare files on your computer to these databases to identify malicious files.
- Updates: Antivirus software requires frequent updates to stay effective. These updates ensure the program recognizes the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
- Behavior Analysis: Some antivirus software includes behavior analysis, which looks for suspicious activities or patterns of behavior that might indicate a new or unknown threat.
Antivirus software is not a guarantee of absolute security, but it significantly reduces your vulnerability to known threats. It's an essential tool for anyone using a computer connected to the internet.
Choosing the Right Antivirus Program
Selecting the right antivirus program is crucial for effective protection. Not all antivirus software is created equal, and the best choice for you depends on several factors. When choosing an antivirus program, consider the following:
- Detection Rate: Look for antivirus software with a high detection rate. This indicates how effectively the program can identify and remove threats.
- System Performance Impact: Some antivirus programs can slow down your computer's performance. Opt for software that has a minimal impact on system resources.
- User Interface: A user-friendly interface makes it easier to navigate and use the software. Look for antivirus programs with an interface that you find intuitive and easy to understand.
- Additional Features: Some antivirus software includes features beyond basic virus scanning. Consider whether you need extras like a firewall, anti-phishing tools, parental controls, or a password manager.
- Cost: There are both free and paid antivirus programs available. While free options can provide good protection, paid programs often offer more features and dedicated customer support.
Installing and Configuring Your Antivirus Software
Once you've chosen an antivirus program, you'll need to install and configure it properly to ensure maximum protection. Here are the steps to install and configure your antivirus software:
- Download and Install: Visit the official website of your chosen antivirus software and download the installer. Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
- Registration and Activation: Many antivirus programs require registration and activation. This may involve creating an account with the antivirus provider and entering a license key or activation code.
- Update the Virus Definitions: After installation, your antivirus program will update its virus definitions to ensure it recognizes the latest threats. Allow the software to complete this process.
- Perform an Initial Scan: Run an initial scan of your computer to check for any existing threats. Depending on the program, this may be a full system scan or a quick scan of critical areas.
- Configure Real-Time Protection: Ensure that real-time protection is active. This feature continuously monitors your computer for threats. You can usually find it in the settings or preferences menu.
- Scheduled Scans: Set up scheduled scans to run at times when your computer is typically not in use. Daily or weekly scans are common options.
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates to keep your antivirus program's virus definitions and software up to date. Regular updates are vital for staying protected against new threats.
- Customize Settings: Depending on your specific needs, you may want to customize the settings of your antivirus program. This can include adjusting the sensitivity of the scans, configuring firewall rules, and setting up email scanning.
Watch the video below to get a better understanding
By following these steps, you'll ensure that your antivirus software is correctly installed and configured to provide robust protection against viruses and malware.
2. Keeping Your Operating System Updated
Operating system (OS) updates are essential for maintaining the security and functionality of your computer. These updates include patches, security fixes, and new features. Here's why keeping your OS up to date is crucial:
- Security Patches: OS updates often include patches for known vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals actively seek these vulnerabilities to exploit them, making timely updates a critical defense against attacks.
- Bug Fixes: Updates address system bugs and glitches that can affect your computer's performance and stability. By installing updates, you can experience a smoother and more reliable computing experience.
- New Features and Improvements: OS updates may introduce new features, enhance compatibility with software and hardware, and provide performance improvements. Staying up to date ensures you can benefit from these enhancements.
- Application Compatibility: As new software and applications are developed, they may require a more recent OS version. To maintain compatibility with the latest software, you need to update your OS.
How to Update Your OS Safely
Updating your OS is a straightforward process, but it's important to do it safely to avoid potential issues. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to update your OS securely:
- Backup Your Data: Before starting any OS update, it's advisable to back up your important data. While the update process is generally safe, unexpected issues can occasionally occur.
- Connect to a Secure Network: Ensure that you are connected to a secure and reliable network with a stable internet connection. Updates can be large, so a stable connection is crucial to prevent interruptions during the download.
- Check for Updates: Depending on your OS, you can usually find the update option in the system settings or control panel. It may be labeled as "Software Update" (on macOS), "Windows Update" (on Windows), or something similar on other systems. Check for available updates.
- Download and Install: When updates are available, download and install them. The process may take some time, so be patient and avoid interrupting it.
- Restart Your Computer: Some updates may require a system restart to apply changes fully. If prompted, restart your computer.
- Keep Automatic Updates Enabled: To ensure ongoing security and performance improvements, leave automatic updates enabled. This way, your OS will automatically check for and install updates when they become available.
- Check for Driver Updates: In addition to OS updates, it's a good practice to check for driver updates for your hardware components, such as graphics cards and network adapters. Updated drivers can improve performance and stability.
- Secure Your OS: Beyond updating, maintain a secure OS by enabling a firewall, using strong passwords, and being cautious when downloading and installing software.
By following these steps, you'll keep your operating system up to date, which is a fundamental aspect of protecting your computer from viruses and other security threats.
3. Implementing Strong Passwords and Authentication
The use of strong, unique passwords is a fundamental aspect of computer security. Strong passwords are a vital defense against unauthorized access to your accounts and data. Here are some password best practices to help you create and maintain secure passwords:
- Complexity: Create passwords that are complex and not easily guessable. A strong password typically includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Uniqueness: Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts. Each account should have a unique password to prevent a security breach on one account from compromising others.
- Length: Longer passwords are generally more secure. Aim for a minimum of 12 characters in your passwords.
- Avoid Personal Information: Do not use easily accessible information like birthdays, names, or common words in your passwords. Hackers can easily guess such information.
- Passphrases: Consider using passphrases, which are longer combinations of words, numbers, and symbols. These can be both strong and memorable.
- Regular Updates: Change your passwords periodically, especially for critical accounts like email, online banking, and social media.
- Use a Password Manager: Password managers can generate, store, and autofill complex passwords for you, eliminating the need to remember them all.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Whenever possible, enable MFA for your accounts. MFA requires an additional verification step, such as a code sent to your mobile device, making it significantly more secure.
- Security Questions: Be cautious with security questions, as the answers may be easily discoverable. Use fake answers or answers that only you would know.
- Avoid Dictionary Words: Refrain from using whole words found in the dictionary. Hackers often use dictionary attacks to guess passwords.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring two forms of verification: something you know (your password) and something you have (a mobile device or authentication app). Here's how to enable and use 2FA:
- Check Account Support: Start by checking if the accounts you use offer 2FA. Many online services, such as email providers and social media platforms, provide this feature.
- Enable 2FA: Access your account's security settings and enable 2FA. This typically involves linking your account to a mobile device or authentication app.
- Verification Codes: With 2FA enabled, you'll receive verification codes on your mobile device when you log in. Enter these codes in addition to your password to access your account.
- Backup Codes: Some services offer backup codes in case you lose access to your mobile device. Store these codes in a safe place.
- Authentication Apps: Instead of receiving SMS codes, you can use authentication apps like Google Authenticator or Authy. These apps generate time-based codes that you enter when logging in.
Password Manager Tools
Password manager tools are highly useful for generating and managing secure passwords. These tools offer several advantages:
- Password Generation: Password managers can create complex and random passwords that are virtually impossible for hackers to guess.
- Storage and Organization: They securely store your passwords in an encrypted database, so you don't have to remember them all.
- Autofill: Password managers can automatically fill in login information for websites and applications, making it more convenient for you to use strong passwords.
- Synchronization: Many password managers offer synchronization across multiple devices, ensuring your passwords are accessible when and where you need them.
- Security: Password manager databases are encrypted and require a master password for access. Make sure your master password is strong and memorable.
- Password Change Management: Password managers can help you change your passwords at regular intervals.
Popular password managers include LastPass, 1Password, Dashlane, and Bitwarden. Choose one that suits your needs and follow their instructions for installation and setup.
Implementing strong passwords and two-factor authentication significantly enhances the security of your accounts and helps protect your computer from unauthorized access and data breaches.
4. Avoiding Suspicious Websites
One of the primary ways viruses and malware can infect your computer is through malicious websites. Here are some practices to help you avoid suspicious websites and maintain safe browsing habits:
- Check Website URLs: Before visiting a website, examine the URL. Look for the "https://" prefix, which indicates a secure connection. Be cautious of websites with misspelled URLs or extra characters that could be fake copies of legitimate sites.
- Use Browser Extensions: Consider installing browser extensions that provide website reputation and security information. These tools can alert you to potentially harmful websites.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest online threats and scams. Awareness can help you recognize common signs of suspicious websites.
- Online Tools: Use online tools like Google's Safe Browsing tool to check if a website is safe. Many antivirus programs also offer browser extensions that provide real-time safety assessments.
- Review Privacy Policies: Before interacting with a website, review its privacy policy and terms of use. Ensure you are comfortable with how your data will be handled.
- Ad Blockers: Ad blockers can prevent malicious ads and pop-ups from displaying on websites, reducing the risk of accidental clicks on harmful content.
- Common Sense: Trust your instincts. If a website seems too good to be true or asks for excessive personal information, be cautious.
- Keep Browsers Updated: Regularly update your web browser to ensure you have the latest security features and patches.
Safe Downloading and File Sharing
Downloading files from untrusted sources can expose your computer to viruses and malware. Follow these safe downloading and file-sharing practices:
- Verify the Source: Download files only from trusted sources. Official websites and well-known app stores are typically safe.
- Check File Extensions: Be cautious of files with unusual or mismatched file extensions. For example, a file with a .exe extension disguised as a .pdf is suspicious.
- Use Download Links: Avoid clicking on ads that prompt downloads. Instead, use the official download links provided on websites.
- Torrenting Risks: If you use torrenting, be aware of the associated risks. Torrented files can often contain malware. Only download from reputable sources, and use caution.
- Verify Files with Antivirus: Run downloaded files through your antivirus software before opening them.
- Email Attachments: Don't download email attachments from unknown or suspicious sources. Scan email attachments with your antivirus software.
- Peer-to-Peer Sharing: If you use peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing networks, be cautious. These networks can be rife with malware. Scan downloaded files and use a firewall to restrict unauthorized access.
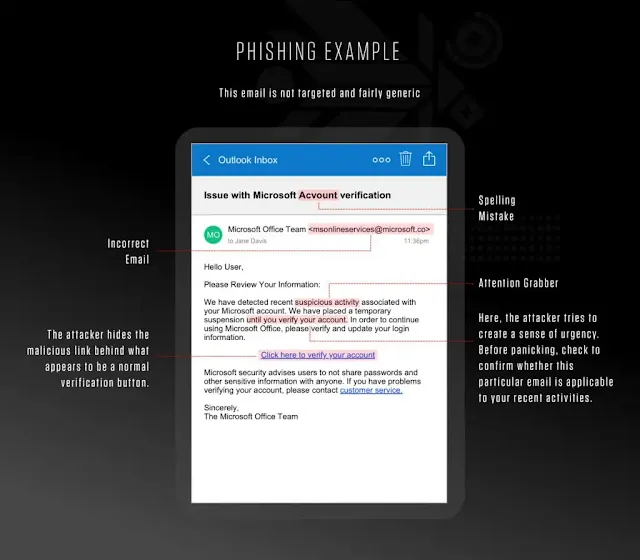
Phishing Awareness
Phishing is a common method used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into revealing personal information. Enhance your awareness of phishing attacks by following these guidelines:
- Check Sender Identity: Verify the sender's email address before opening any email or clicking on links. Be wary of email addresses that appear suspicious or unfamiliar.
- Beware of Urgency: Phishing emails often create a sense of urgency to prompt immediate action. Take your time to evaluate the legitimacy of the request.
- Check Hyperlinks: Hover your cursor over hyperlinks in emails without clicking to see where they lead. Ensure they match the sender's claimed identity and are from reputable domains.
- Look for Misspellings and Grammar Mistakes: Phishing emails often contain spelling and grammar errors. Be on the lookout for these signs.
- Avoid Downloading Attachments: Don't download attachments from emails unless you are certain of the sender's identity. Malicious attachments can contain viruses or malware.
- Verify Requests for Personal Information: Be cautious about providing personal or financial information in response to email requests. Legitimate organizations rarely ask for such information via email.
By following safe browsing habits and being vigilant, you can significantly reduce the risk of encountering viruses and malware through websites, downloads, and phishing attempts.
5. Identifying Suspicious Emails
Email is a common vector for malware distribution, and being able to identify suspicious emails is essential for maintaining your computer's security. Here are key steps to help you identify potentially harmful emails:
- Check the Sender: Verify the sender's email address. Be cautious of emails from unfamiliar or unofficial addresses.
- Subject Line: Examine the subject line. Emails with vague or overly urgent subject lines may be suspicious.
- Attachments: Be wary of email attachments, especially if they come from unknown sources. Avoid opening them unless you can confirm their safety.
- Links: Hover your cursor over links in the email to preview the URL without clicking. Ensure that the links match the sender's identity and lead to secure websites.
- Spelling and Grammar: Poor grammar and spelling mistakes in the email's content can be a sign of phishing.
- Sender's Request: Watch out for requests for personal information, financial details, or other sensitive data. Legitimate organizations typically do not request such information via email.
- Use Anti-Phishing Tools: Many email clients and antivirus programs offer built-in anti-phishing tools that can identify and filter out suspicious emails.
Avoiding Email Attachments from Unknown Sources
Email attachments can contain viruses or malware. To stay secure, avoid opening email attachments from unknown sources. Here are additional steps to ensure email attachment safety:
- Verify the Sender: If you receive an attachment from a known sender but the email seems unusual, contact the sender directly to confirm they intended to send the attachment.
- Use an Email Scanner: Many antivirus programs provide email scanning features that automatically check attachments for malware.
- Check File Types: Be cautious of executable file types (e.g., .exe, .bat) in attachments. Malicious software is often hidden in these formats.
- Educate Users: Educate users in your organization about email security best practices to reduce the risk of email-based malware infections.
By following these guidelines, you can bolster your email security, minimizing the risk of encountering malicious attachments or phishing emails.
6. Regular Backups
Backups are your safety net in case of a virus infection or other data loss events. By regularly creating backups of your important files and data, you ensure that, even in the worst-case scenario, you can recover your information. Here's why backups are crucial:
- Data Recovery: Backups provide a means to recover lost or compromised data, whether due to a virus infection, hardware failure, or accidental deletion.
- Minimized Downtime: With proper backups in place, you can quickly restore your computer to a functional state, reducing downtime and maintaining productivity.
- Protection from Ransomware: In the event of a ransomware attack, where your files are encrypted and held hostage, having backups means you won't have to pay the ransom to regain access.
- Peace of Mind: Backups offer peace of mind, knowing that your important data is safe and can be easily recovered if needed.
How to Create Reliable Backups
Creating reliable backups is a straightforward process. Here's how to set up and maintain effective backup routines:
- Select a Backup Solution: Choose a backup solution that suits your needs. Options include external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS) devices, and cloud-based storage services.
- Regular Scheduling: Set up a regular backup schedule to ensure that your data is consistently backed up. Daily or weekly backups are common choices.
- Automate the Process: Most backup solutions offer automation features, so you don't have to remember to initiate backups manually.
- Use Incremental Backups: Consider using incremental backups, which only back up the changes made since the last backup. This approach is more efficient in terms of storage space and time.
- Secure Backup Data: Ensure that your backup data is stored securely. If you use external drives, keep them in a safe location. For cloud-based backups, use strong, unique passwords and two-factor authentication for added security.
- Test Your Restorations: Periodically test the restoration process to ensure that you can successfully recover your data. This practice helps identify and address any issues with your backups.
- Document Your Backup Strategy: Keep a record of your backup strategy, including what is backed up, when, and where. This documentation will be invaluable in the event of data loss.
By following these guidelines, you'll establish a reliable backup system that safeguards your data and ensures you can recover it in case of a virus infection or other data loss events.
8. Firewall Protection
What Is a Firewall?
A firewall is a critical component of your computer's security system. It acts as a barrier between your computer and the internet, filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic based on a set of rules. The firewall's primary purpose is to allow safe traffic to pass through while blocking or monitoring potentially harmful traffic.
There are two main types of firewalls:
- Software Firewalls: These firewalls are installed on your computer and provide protection for that specific device. They can filter both incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Hardware Firewalls: Hardware firewalls are physical devices placed between your computer and the internet, typically within a network or router. They protect all devices connected to the network.
Configuring Your Firewall Settings
Properly configuring your firewall settings is essential for maximizing its effectiveness. Here are steps to configure your firewall securely:
- Default Settings: Start with the default settings provided by your firewall software or hardware. These settings are often configured to offer a good balance between security and usability.
- Application Rules: Many firewalls allow you to set rules for specific applications or services. Configure these rules to allow or block network access for different programs as needed.
- Port Configuration: Be cautious when configuring port settings, as improper configuration can leave your computer vulnerable to attacks. Only open ports that are necessary for the services you use.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Some firewalls include intrusion detection and prevention features. These can help identify and block suspicious network activity.
- Regular Updates: Keep your firewall software up to date. Updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities.
- VPN and Proxy Settings: If you use a virtual private network (VPN) or proxy, ensure that your firewall is compatible and configured to work with these services.
- Log Analysis: Review firewall logs to monitor network traffic and identify any unusual or suspicious activity.
- Regular Testing: Periodically test your firewall to ensure that it is functioning correctly and blocking unauthorized traffic.
Firewalls provide an additional layer of protection for your computer and are an essential part of a comprehensive security strategy.
9. Safe Social Media Practices
Social media platforms are a common target for cyberattacks and data breaches. Ensuring that your privacy settings are correctly configured is a crucial aspect of protecting your computer and personal information. Here are steps to improve your privacy settings:
- Review Privacy Settings: Periodically review and adjust your privacy settings on social media platforms. These settings control who can see your posts, personal information, and more.
- Limit Public Posts: Consider setting the default visibility of your posts to "Friends" or another restricted audience. Avoid making all your posts public, which can expose your information to a wider audience.
- Review App Permissions: Check the permissions granted to third-party applications connected to your social media accounts. Revoke access for apps you no longer use or trust.
- Location Privacy: Be cautious about sharing your precise location, especially if it is not necessary for your social media activities. Use location tagging sparingly.
- Audit Friends and Contacts: Regularly review your list of friends or contacts and remove individuals you no longer wish to connect with.
- Review Tagging: Configure settings to control who can tag you in photos and posts. This can help you manage what appears on your profile.
Recognizing Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks are attempts to manipulate individuals into revealing confidential information or taking specific actions. Social media is a common platform for these attacks. Recognizing the signs of social engineering can help you avoid falling victim:
- Be Cautious of Unsolicited Messages: If you receive unsolicited messages or friend requests, particularly from unknown individuals, exercise caution. Verify the identity of the sender before engaging with them.
- Check for Red Flags: Be on the lookout for common red flags such as messages that create a sense of urgency, requests for personal or financial information, and offers that seem too good to be true.
- Verify Links and Downloads: Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from social media, especially if you did not expect to receive them.
- Use Strong Authentication: Enable strong authentication measures, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), on your social media accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest social engineering tactics and scams. Knowledge is your best defense against these attacks.
By practicing safe social media habits and staying vigilant, you can reduce the risk of falling victim to social engineering attacks that could compromise your computer's security.
10. Dealing with Suspicious Activity
Viruses and malware can exhibit various signs that your computer may be compromised. Recognizing these signs promptly is vital for taking action. Common signs of infection include:
- Slow System Performance: A sudden and noticeable decline in your computer's speed and performance can be a sign of malware or a virus.
- Unexpected Pop-Ups: Persistent and intrusive pop-up advertisements, especially when you're not browsing the web, are often caused by malware.
- Altered Browser Settings: If your browser's homepage, search engine, or new tab page has changed without your consent, it may be due to malware.
- Unexplained File Changes: If files or folders have been altered, deleted, or encrypted without your knowledge, this is a clear sign of a potential virus infection.
- High Network Activity: Unexplained and continuous network activity, especially when your computer should be idle, can indicate malicious activity.
What to Do if Your Computer Is Infected
If you suspect your computer is infected with a virus or malware, it's essential to take immediate action to mitigate the damage and remove the threat. Here are the steps to follow:
- Disconnect from the Internet: Disconnect your computer from the internet to prevent the malware from communicating with its source or spreading further.
- Run a Full Antivirus Scan: Initiate a full system scan with your antivirus software. Allow the software to detect and remove any threats it identifies.
- Follow Removal Instructions: Follow any specific removal instructions provided by your antivirus software. Some infections may require additional steps for complete removal.
- Update Your Software: Ensure that your operating system and all installed software are up to date with the latest security patches. Vulnerabilities in outdated software can be exploited by malware.
- Change Your Passwords: Change your passwords for critical accounts, especially if you suspect that malware may have captured your login credentials.
- Seek Professional Help: If the infection persists or if you are unable to remove it on your own, consider seeking assistance from a professional computer security expert.
Remember that early detection and action are key to minimizing the damage caused by a virus or malware infection. Staying vigilant and promptly addressing security issues will help protect your computer and your data.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we've covered the essential strategies and practices to protect your computer from viruses and malware. Computer security is an ongoing process, and by following the recommendations provided here, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these digital threats. Vigilance, education, and the right tools are your best allies in maintaining a secure digital environment.
By understanding computer viruses, using antivirus software, keeping your operating system updated, implementing strong passwords and two-factor authentication, practicing safe browsing and email habits, and being cautious on social media, you can fortify your computer's defenses against the ever-evolving world of cyber threats. Regular backups, firewall protection, and quick response to suspicious activity will further enhance your security. Stay proactive, stay secure.






.webp)




Post a Comment